Easing Chronic Pain: The Role of Reducing Inflammation
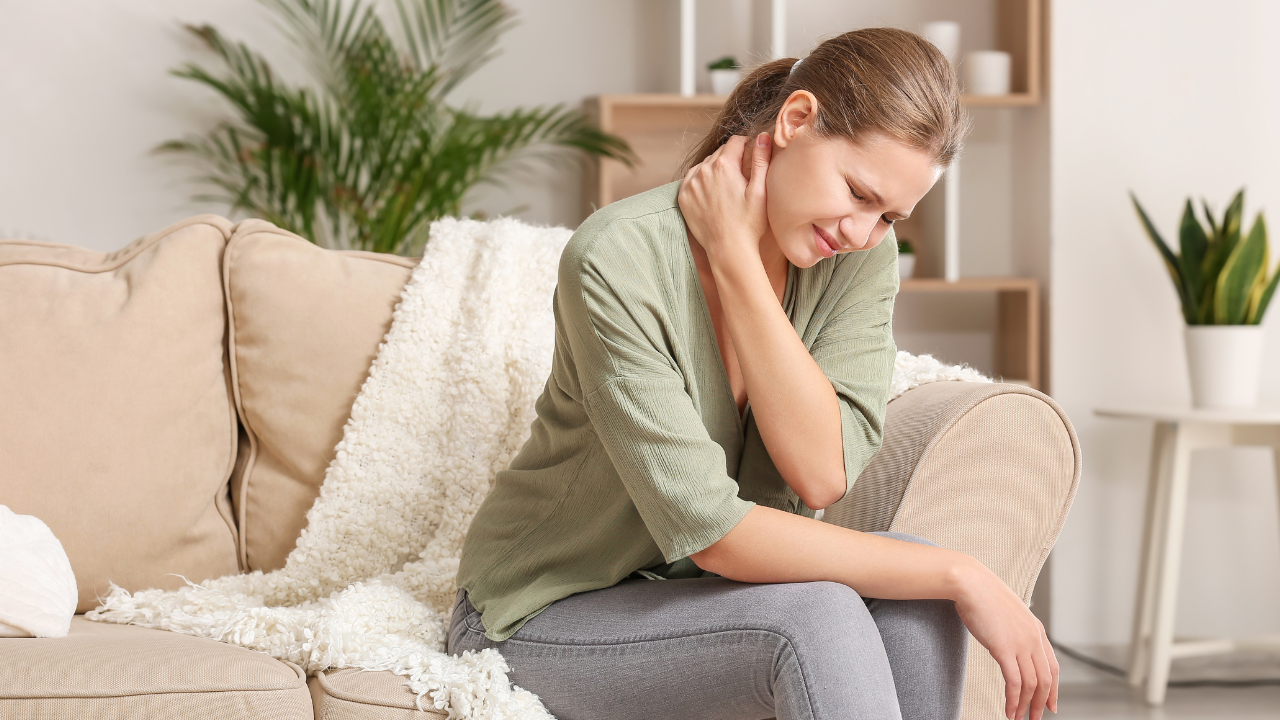
Chronic pain can be an overwhelming and debilitating condition, impacting every aspect of a person's life. However, understanding the significant role inflammation plays in chronic pain can be a game-changer for those seeking relief. This blog post will delve into the relationship between chronic pain and inflammation and explore how reducing inflammation can help ease chronic pain.
Understanding Chronic Pain and Inflammation
Chronic pain is defined as pain that lasts longer than three months or beyond the usual healing time of an injury. It can stem from various causes, including injuries, diseases, conditions like arthritis, or nerve damage.
Inflammation, on the other hand, is our body's natural response to injury or infection. It's a protective measure aimed at removing harmful stimuli and initiating the healing process. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can lead to persistent pain and tissue damage.
The link between chronic pain and inflammation is strong. Many forms of chronic pain, such as arthritis or fibromyalgia, are associated with high levels of systemic inflammation.
How Reducing Inflammation Can Help
Research shows that reducing systemic inflammation can significantly impact chronic pain management. Here's why:
-
Alleviating Pain at the Source:
-
When inflammation is reduced, the underlying cause of the pain is directly addressed. This can result in a decrease in swelling and tenderness, providing relief from the pain.
-
-
Preventing Further Damage:
-
By curbing inflammation, we can prevent further damage to tissues and organs that can exacerbate chronic pain conditions. This preventive measure can help manage pain in the long term.
-
-
Enhancing Mobility:
-
Reduced inflammation often leads to improved mobility in individuals suffering from chronic pain. This can make daily tasks less painful and improve overall quality of life.
-
Strategies to Reduce Inflammation
There are several strategies one can employ to reduce inflammation and, in turn, manage chronic pain:
-
Diet and Nutrition:
-
A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and healthy fats can help reduce inflammation. Conversely, limiting consumption of processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can also help curb inflammation.
-
-
Exercise:
-
Regular physical activity has been shown to reduce inflammation over time. Even low-impact exercises like walking or swimming can have significant anti-inflammatory effects.
-
-
Medication and Supplements:
-
Certain medications and supplements, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and omega-3 fatty acids, can help reduce inflammation.
-
-
Stress Management:
-
Stress can trigger inflammatory responses in the body, so managing stress through techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can help reduce inflammation.
-
Conclusion
Understanding the link between chronic pain and inflammation is vital for effective pain management. By focusing on reducing inflammation, individuals suffering from chronic pain can find a path towards relief and improved quality of life.